An Introduction to Business Views
A business view contains database connections and relationships between view elements. This topic describes the four types of objects in a business view: category objects, group objects, aggregation objects, and detail objects.
A between view shields report end users from having to understand the underlying structure of a data source, and enables them to create complex reports containing multiple components and analyze data based on a set of view elements they can understand. All reports created from a business view automatically include all of the interactivity built into that business view. For example, they can include things like drill down, drill up so that end users are able to switch data from one group to another.
To make use of business views at server runtime, you need to define them in Report Designer in advance and then publish them to Report Server. For more information, see Working with Business Views in the Report Designer Guide.
A business view may contain category objects and the following view elements: group objects, aggregation objects, and detail objects.
- Category objects
Category objects contain a collection of view elements. A business view may contain more than one category. The icon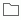 indicates that an object is a category. Categories are only for categorizing view elements, and you cannot insert categories into reports. Categories often indicate the names of the underlying DBMS tables.
indicates that an object is a category. Categories are only for categorizing view elements, and you cannot insert categories into reports. Categories often indicate the names of the underlying DBMS tables. - Group objects
Group objects are view elements that become the basis for analysis in a report. They characteristically return text or date values. The icon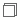 indicates that an object is a group object. You can insert a group object as a column or row field in a crosstab, as a group field or detail field in a table or banded object, or as category/series field in a chart.
indicates that an object is a group object. You can insert a group object as a column or row field in a crosstab, as a group field or detail field in a table or banded object, or as category/series field in a chart. - Aggregation objects
Aggregation objects are numeric view elements that are calculated dynamically at runtime. The icon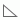 indicates that an object is an aggregation object. You can insert an aggregation object into the group header or footer in a table or banded object, or into a crosstab as an aggregate field. You can also use an aggregation object as a detail field in a table. Web Report Studio calculates the summary values based on the group level that the aggregation object is at. An aggregation object is the only object that can provide the value on a chart.
indicates that an object is an aggregation object. You can insert an aggregation object into the group header or footer in a table or banded object, or into a crosstab as an aggregate field. You can also use an aggregation object as a detail field in a table. Web Report Studio calculates the summary values based on the group level that the aggregation object is at. An aggregation object is the only object that can provide the value on a chart. - Detail objects
Detail objects provide additional information. The icon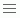 indicates that an object is a detail object. You can insert a detail object into a table or banded object as a detail field.
indicates that an object is a detail object. You can insert a detail object into a table or banded object as a detail field.
 Previous Topic
Previous Topic
 Back to top
Back to top